|
Learning Target:
I can explain the causes of the Great Depression, & I can describe its effects on ordinary Americans. Critical Vocabulary: Recession, Isolationism, Interventionism, Frederick W. Taylor, “Return to Normalcy,” Warren G. Harding, Albert Fall, Teapot Dome Scandal, "Ohio Gang," John Maynard Keynes, Calvin Coolidge, American Legion, Kellogg-Briand Pact, Dawes Plan of 1924, Herbert Hoover, Al Smith, Stock Market Crash of 1929, Speculation, Reconstruction Finance Corporation, Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act, Bonus Army, Election of 1932, Franklin D. Roosevelt, "Brain Trust," New Deal, Bank Holiday, Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, "Fireside Chats," “Relief, Recovery, and Reform,” Unemployment Relief Act, Civilian Conservation Corps, Federal Emergency Relief Act, Civil Works Administration, Agricultural Adjustment Act, Butler v. U.S., Dust Bowl, Twenty-first Amendment, Securities and Exchange Commission, Tennessee Valley Authority, Federal Housing Administration, National Recovery Administration, Public Works Administration, Works Progress Administration, Wagner Act, National Labor Relations Board, Social Security Act of 1935, Father Charles Coughlin, Senator Huey Long, "Share Our Wealth," Dr. Francis Townsend, American Liberty League, Alfred Landon, Twentieth Amendment, “Court-Packing” Scheme, Fair Labor Standards Act Today's Agenda:
Homework: The Great Depression Reading
0 Comments
Learning Target:
I can explain the causes of the Great Depression, & I can describe its effects on ordinary Americans. Critical Vocabulary: Recession, Isolationism, Interventionism, Frederick W. Taylor, “Return to Normalcy,” Warren G. Harding, Albert Fall, Teapot Dome Scandal, "Ohio Gang," John Maynard Keynes, Calvin Coolidge, American Legion, Kellogg-Briand Pact, Dawes Plan of 1924, Herbert Hoover, Al Smith, Stock Market Crash of 1929, Speculation, Reconstruction Finance Corporation, Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act, Bonus Army, Election of 1932, Franklin D. Roosevelt, "Brain Trust," New Deal, Bank Holiday, Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, "Fireside Chats," “Relief, Recovery, and Reform,” Unemployment Relief Act, Civilian Conservation Corps, Federal Emergency Relief Act, Civil Works Administration, Agricultural Adjustment Act, Butler v. U.S., Dust Bowl, Twenty-first Amendment, Securities and Exchange Commission, Tennessee Valley Authority, Federal Housing Administration, National Recovery Administration, Public Works Administration, Works Progress Administration, Wagner Act, National Labor Relations Board, Social Security Act of 1935, Father Charles Coughlin, Senator Huey Long, "Share Our Wealth," Dr. Francis Townsend, American Liberty League, Alfred Landon, Twentieth Amendment, “Court-Packing” Scheme, Fair Labor Standards Act Today's Agenda:
Learning Target:
I can summarize Harding, Coolidge, & Hoover's fiscal policies, & I can evaluate their effects on the national economy. Critical Vocabulary: Recession, Isolationism, Interventionism, Frederick W. Taylor, “Return to Normalcy,” Warren G. Harding, Albert Fall, Teapot Dome Scandal, "Ohio Gang," John Maynard Keynes, Calvin Coolidge, American Legion, Kellogg-Briand Pact, Dawes Plan of 1924, Herbert Hoover, Al Smith, Stock Market Crash of 1929, Speculation, Reconstruction Finance Corporation, Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act, Bonus Army, Election of 1932, Franklin D. Roosevelt, "Brain Trust," New Deal, Bank Holiday, Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, "Fireside Chats," “Relief, Recovery, and Reform,” Unemployment Relief Act, Civilian Conservation Corps, Federal Emergency Relief Act, Civil Works Administration, Agricultural Adjustment Act, Butler v. U.S., Dust Bowl, Twenty-first Amendment, Securities and Exchange Commission, Tennessee Valley Authority, Federal Housing Administration, National Recovery Administration, Public Works Administration, Works Progress Administration, Wagner Act, National Labor Relations Board, Social Security Act of 1935, Father Charles Coughlin, Senator Huey Long, "Share Our Wealth," Dr. Francis Townsend, American Liberty League, Alfred Landon, Twentieth Amendment, “Court-Packing” Scheme, Fair Labor Standards Act Today's Agenda:
Homework: The Great Depression Reading Learning Target:
I can summarize Harding, Coolidge, & Hoover's fiscal policies, & I can evaluate their effects on the national economy. Critical Vocabulary: Recession, Isolationism, Interventionism, Frederick W. Taylor, “Return to Normalcy,” Warren G. Harding, Albert Fall, Teapot Dome Scandal, "Ohio Gang," John Maynard Keynes, Calvin Coolidge, American Legion, Kellogg-Briand Pact, Dawes Plan of 1924, Herbert Hoover, Al Smith, Stock Market Crash of 1929, Speculation, Reconstruction Finance Corporation, Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act, Bonus Army, Election of 1932, Franklin D. Roosevelt, "Brain Trust," New Deal, Bank Holiday, Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, "Fireside Chats," “Relief, Recovery, and Reform,” Unemployment Relief Act, Civilian Conservation Corps, Federal Emergency Relief Act, Civil Works Administration, Agricultural Adjustment Act, Butler v. U.S., Dust Bowl, Twenty-first Amendment, Securities and Exchange Commission, Tennessee Valley Authority, Federal Housing Administration, National Recovery Administration, Public Works Administration, Works Progress Administration, Wagner Act, National Labor Relations Board, Social Security Act of 1935, Father Charles Coughlin, Senator Huey Long, "Share Our Wealth," Dr. Francis Townsend, American Liberty League, Alfred Landon, Twentieth Amendment, “Court-Packing” Scheme, Fair Labor Standards Act Today's Agenda:
Homework: The Great Depression Reading
Learning Target:
I can discuss the political, social, economic, & religious tensions that divided Americans during the 1920s. Critical Vocabulary: Mitchell Palmer, “Red Scare,” General Intelligence Division, “Soviet Ark,” “Palmer Raids,” Emergency Quota Act of 1921, Sacco and Vanzetti Trial, John Dewey, John T. Scopes, “Monkey Trial,” Clarence Darrow, Eighteenth Amendment, Volstead Act, “Speakeasies,” “Bootleg,” Al Capone, “Jazz Age,” Nineteenth Amendment, League of Women Voters, “New Woman,” “Flappers,” “Duke” Ellington, Cotton Club, “Harlem Renaissance,” Marcus Garvey, “Back to Africa Movement,” Claude McKay, Langston Hughes, Zora Neale Hurston, Gertrude Stein, F. Scott Fitzgerald, Ernest Hemingway, William Faulkner, T. S. Eliot, Ford Motor Company, Model T, Frederick Taylor, “Babe” Ruth, The Jazz Singer, Rudolph Valentino, Clara Bow Today's Agenda:
Homework: The Roaring Twenties Reading
Learning Target:
I can discuss the political, social, economic, & religious tensions that divided Americans during the 1920s. Critical Vocabulary: Mitchell Palmer, “Red Scare,” General Intelligence Division, “Soviet Ark,” “Palmer Raids,” Emergency Quota Act of 1921, Sacco and Vanzetti Trial, John Dewey, John T. Scopes, “Monkey Trial,” Clarence Darrow, Eighteenth Amendment, Volstead Act, “Speakeasies,” “Bootleg,” Al Capone, “Jazz Age,” Nineteenth Amendment, League of Women Voters, “New Woman,” “Flappers,” “Duke” Ellington, Cotton Club, “Harlem Renaissance,” Marcus Garvey, “Back to Africa Movement,” Claude McKay, Langston Hughes, Zora Neale Hurston, Gertrude Stein, F. Scott Fitzgerald, Ernest Hemingway, William Faulkner, T. S. Eliot, Ford Motor Company, Model T, Frederick Taylor, “Babe” Ruth, The Jazz Singer, Rudolph Valentino, Clara Bow Today's Agenda:
Homework: The Roaring Twenties Reading Learning Target:
I can discuss the political, social, economic, & religious tensions that divided Americans during the 1920s. Critical Vocabulary: Mitchell Palmer, “Red Scare,” General Intelligence Division, “Soviet Ark,” “Palmer Raids,” Emergency Quota Act of 1921, Sacco and Vanzetti Trial, John Dewey, John T. Scopes, “Monkey Trial,” Clarence Darrow, Eighteenth Amendment, Volstead Act, “Speakeasies,” “Bootleg,” Al Capone, “Jazz Age,” Nineteenth Amendment, League of Women Voters, “New Woman,” “Flappers,” “Duke” Ellington, Cotton Club, “Harlem Renaissance,” Marcus Garvey, “Back to Africa Movement,” Claude McKay, Langston Hughes, Zora Neale Hurston, Gertrude Stein, F. Scott Fitzgerald, Ernest Hemingway, William Faulkner, T. S. Eliot, Ford Motor Company, Model T, Frederick Taylor, “Babe” Ruth, The Jazz Singer, Rudolph Valentino, Clara Bow Today's Agenda:
Homework: The Roaring Twenties Reading Learning Target:
I can discuss the political, social, economic, & religious tensions that divided Americans during the 1920s. Critical Vocabulary: Mitchell Palmer, “Red Scare,” General Intelligence Division, “Soviet Ark,” “Palmer Raids,” Emergency Quota Act of 1921, Sacco and Vanzetti Trial, John Dewey, John T. Scopes, “Monkey Trial,” Clarence Darrow, Eighteenth Amendment, Volstead Act, “Speakeasies,” “Bootleg,” Al Capone, “Jazz Age,” Nineteenth Amendment, League of Women Voters, “New Woman,” “Flappers,” “Duke” Ellington, Cotton Club, “Harlem Renaissance,” Marcus Garvey, “Back to Africa Movement,” Claude McKay, Langston Hughes, Zora Neale Hurston, Gertrude Stein, F. Scott Fitzgerald, Ernest Hemingway, William Faulkner, T. S. Eliot, Ford Motor Company, Model T, Frederick Taylor, “Babe” Ruth, The Jazz Singer, Rudolph Valentino, Clara Bow Today's Agenda:
Homework: The Roaring Twenties Reading Learning Target:
I can discuss the political, social, economic, & religious tensions that divided Americans during the 1920s. Critical Vocabulary: Mitchell Palmer, “Red Scare,” General Intelligence Division, “Soviet Ark,” “Palmer Raids,” Emergency Quota Act of 1921, Sacco and Vanzetti Trial, John Dewey, John T. Scopes, “Monkey Trial,” Clarence Darrow, Eighteenth Amendment, Volstead Act, “Speakeasies,” “Bootleg,” Al Capone, “Jazz Age,” Nineteenth Amendment, League of Women Voters, “New Woman,” “Flappers,” “Duke” Ellington, Cotton Club, “Harlem Renaissance,” Marcus Garvey, “Back to Africa Movement,” Claude McKay, Langston Hughes, Zora Neale Hurston, Gertrude Stein, F. Scott Fitzgerald, Ernest Hemingway, William Faulkner, T. S. Eliot, Ford Motor Company, Model T, Frederick Taylor, “Babe” Ruth, The Jazz Singer, Rudolph Valentino, Clara Bow Today's Agenda:
Homework: The Roaring Twenties Reading Learning Target:
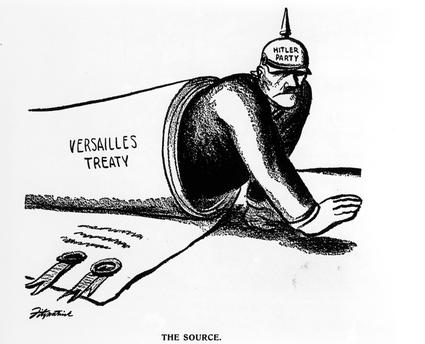
I can describe the events that led the United States into World War I, & I can analyze the war’s impact on American society. Critical Vocabulary: Archduke Franz Ferdinand, Central Powers, Allied Powers, U-boat, Lusitania, Sussex Ultimatum, Election of 1916, Charles Evans Hughes, “peace without victory,” unrestricted submarine warfare, Zimmerman Telegram, Committee on Public Information, George Creel, Food Administration, Herbert Hoover, Fuel Administration, War Industries Board, Bernard Baruch, National War Labor Board, Espionage Act of 1917, Sedition Act of 1918, Industrial Workers of the World, Eugene V. Debs, William D. Haywood, Schenck v. U.S., Oliver Wendell Holmes, “clear and present danger,” American Expeditionary Force, General John Pershing, “doughboys,” Battle of the Argonne Forest, Fourteen Points Address, Big Four, League of Nations, League Covenant, collective security, “war-guilt” clause, reparations, Treaty of Versailles, Henry Cabot Lodge, “reservationists,” “irreconcilables,” “Lodge Reservations,” Election of 1920, “return to normalcy,” Warren G. Harding Today's Agenda:
Homework: World War I Reading |
A life is not important except in the impact it has on other lives.
-Jackie Robinson AnnouncementsApril 20: Prom
April 28: AP Saturday May 3: No School May 9: On Demand Test May 10: AP Exam May 13: Science Test May 21: No School May 27: No School May 30: Last Day Due DatesArchives
May 2019
Visitors |